|
|
|
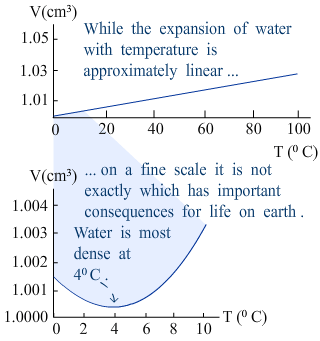 |
For an isotropic (各向同性) solid:
|
|
| |
Thermal stress in a clamped rod |
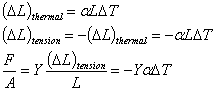 |
|
| |
Quantity of heat |
Heat is the energy transferred between systems of different temperatures.
|
Calorie: the amount of heat to raise the temperature of 1 gram of water from 14.5°C to 15.5°C.
|
1 cal =4.186J |
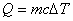 specific heat: c specific heat: c 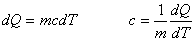 |
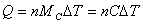 Molar heat capacity: 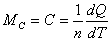 |
 |
| |
Phase changes and calorimetry |
Calorimetry: measuring heat
|
Phase (state of matter): solid, liquid, gas, plasma (等离子体), and Bose-Einstein condensation.
|
Heat of fusion 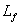 : the heat required to melt 1 kg of solid.
|
Heat of vaporization 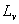 : the heat required to vaporize 1 kg of liquid.
|
Heat of sublimation 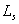 : the heat required to sublime 1 kg of solid directly into gaseous phase. |
Heat of combustion 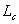 : heat generated to completely combust 1 g of mass.
|
| |
Mechanism of heat transfer |
Conduction: atomic vibration
|
Heat current: rate of heat flow 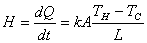 |
Thermal conductivity (热导率): k
|
Thermal resistance: R=L/k
|
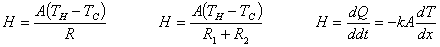 |
|
| |
Convection and radiation |
Convection: heat transported by mass motion from one region of space to another.
|
Radiation: heat transferred by electromagnetic waves (电磁波) |
Stefan-Boltzmann law: 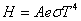 |
Stefan-Boltzmann constant: 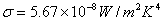 |
Emissivity: e, depends on the nature of the surface.
|
The rate of absorption is also governed by the Stefan-Boltzmann law. The net rate of radiation from a body at T with surroundings at 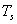 is,
|
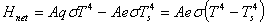 |
For an ideal radiator, e=1. It is also an ideal absorber (black body 黑体).
|
|
