| |
Projectile motioní¬Figure 3.15
|
· A projectile is any body given an initial velocity that then follows a path (trajectory:╣ý╝ú ) determined by the effects of gravity and air resistance.
|
· Begin neglecting resistance.
|
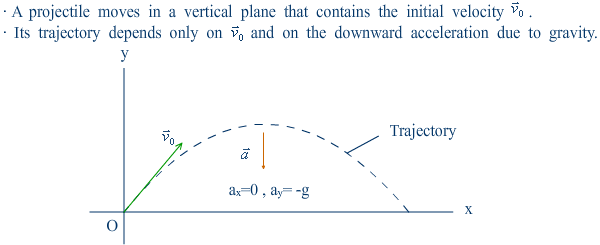 |
| |
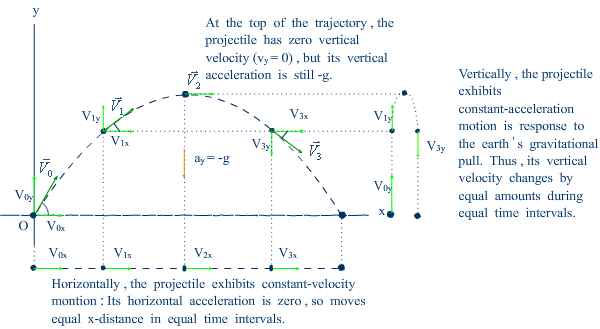
Equations of motion under constant acceleration |
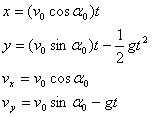 |
The trajectory is a parabola (┼Î╬´¤▀).
Horizontal range (╔ń│╠): 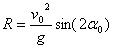
|
 |
| |
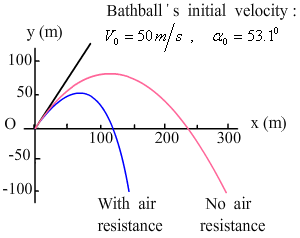
Effects of wind resistanceí¬Figure 3.20 |
|
· Cumulative effects can be large.
· Peak heights and distance fall.
· Trajectories cease to be parabolic.
|
 |
|
