|
|
Thermodynamic process: a process in which the state of a thermodynamic system is changed.
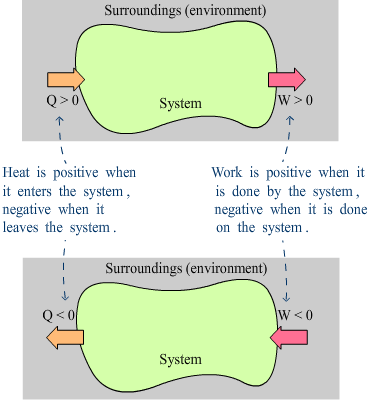
Sign convention:
Q positive when heat flows into the system
Q negative when heat flows out of the system
W positive when the system performs work against its surroundings
W negative when the surroundings perform work against the system
|
 |
|
| |
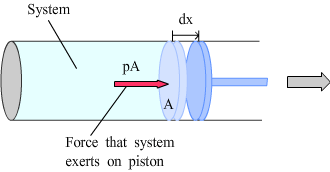
Work done during volume change |
Under constant pressure:
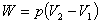 |
 |
|
|
| |
Work done in a thermodynamic process |
Work done by the system depends not only on the initial and final state, but also on the thermodynamic path.
|
|
| |
Heat added in a thermodynamic process |
Heat added to a system also depends the thermodynamic path.
|
isothermal (µÈÎÂ) expansion |
|
free expansion
|
|
| |
Internal energy & the first law of thermodynamics |
Internal energy: the sum of kinetic energies of all constituent particles, plus the sum of all the potential energies of interaction among these particles.
|
First law of thermodynamics: 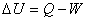 |
The change in internal energy of a system during any thermodynamic process depends only on the initial and final states, not on the thermodynamic path.
|
Internal energy is a state function. |
|
|
