| |
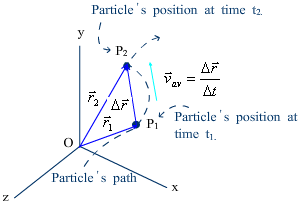
Average velocity¡ªFigure 3.2
|
· Position vector r (x, y, z) is used to locate a particle.
|
· The average velocity between two points will have the same direction as the displacement.
|
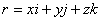
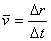
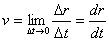
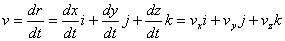
|
 |
| |
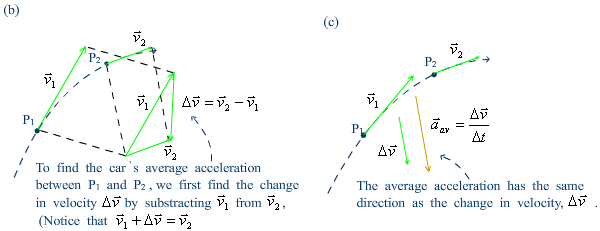
Average acceleration vector¡ªFigure 3.6 |
 |
 |
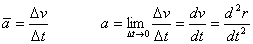 |
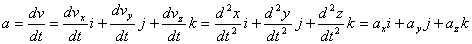 |
| |
Velocity and acceleration¡ªExamples 3.1 and 3.2 |
Example: Average velocity during t=0~2.0 s. |
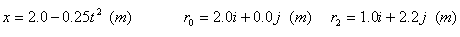 |
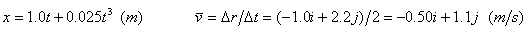 |
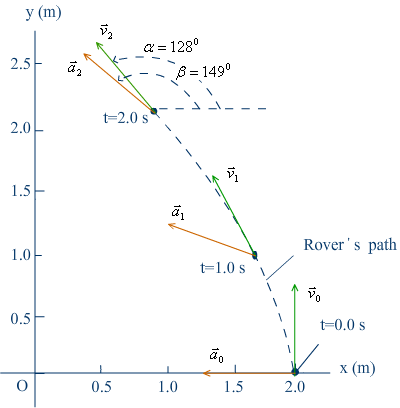 |
Instantaneous velocity at t=2.0 s. 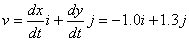 |
Instantaneous acceleration at t=2.0 s. 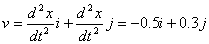 |
| |
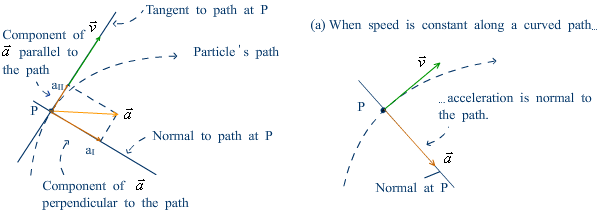
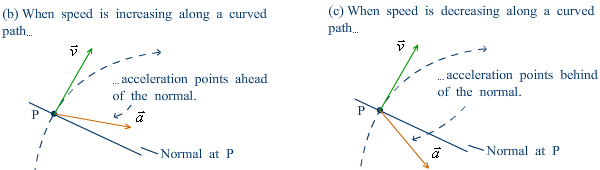
Parallel and perpendicular components of acceleration |
It is more insightful to resolve the acceleration into parallel and perpendicular components.
|
 |
 |
|
