|
Directions for thermodynamic processes
|
Reversible process: any change of state that takes place can be reversed. A system that undergoes a reversible process is always very close to being in thermodynamic equilibrium within itself and with its surroundings. Reversible process is a quasi-equilibrium process.
|
Irreversible processes are nonequilibrium processes, in that the system is not in thermodynamic equilibrium at any point until the end of the process.
|
|
| |
Heat engines |
Heat engine: a device that transforms heat partly into work.
|
The matter inside an engine that undergoes inflow and outflow of heat , expansion and compression, and sometimes change of phase is called working substance.
|
The working substance should undergo cyclic processes in order for the engine to work continuously.
|
All heat engines absorb heat from a source at a relatively high temperature, perform some work, and discard or reject some heat at a lower temperature. The high temperature source is hot reservoir and the low temperature source is cold reservoir. |
For any cyclic process in a heat engine, 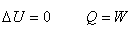 |
| |
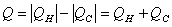
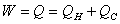
Thermal efficiency of an engine
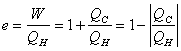
It's impossible to have 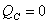
It's impossible to have 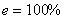
|
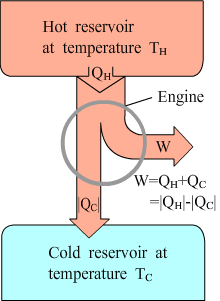 |
|
| |
Otto cycle |
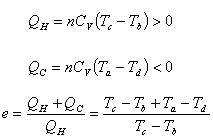
r is the compression ratio: 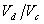
|
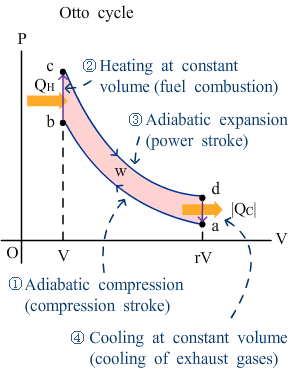 |
|
| |
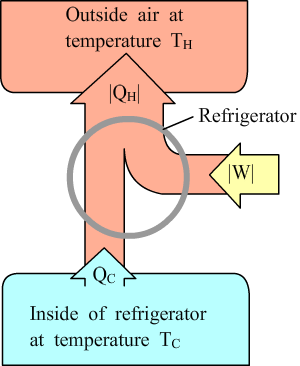
Refrigerators |
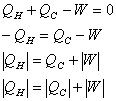
Coefficient of performance:
If the heat current is
and the power is 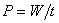 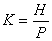 energy efficiency rating (EER) energy efficiency rating (EER)
|
 |
|
|
