|
|
Rigid body does not change its shape and volume when external forces are applied to it. The distance between any two particles does not change when the rigid body moves.
|
|
Translation (平动): all the particles in the rigid body moves in a similar way. They have the same velocities and accelerations. At different times, any arbitrary line within the rigid body moves in a parallel way. The translational motion of a rigid body can be represented by the movement of a single particle.
|
In rotation (转动) around a fixed axis, all the particles in the rigid body take a circular motion around that axis.
|
| |
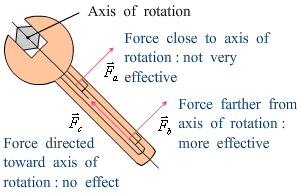
Torque (力矩) |
· A force applied at a right angle to a lever will generate a torque.
· The distance from the pivot to the point of force application will be linearly proportional to the torque produced.
|
 |
|
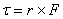 |
A torque is positive if it tends to rotate the body counterclockwise and negative if it tends to rotate the body in the clockwise direction. |
| |
Calculate an applied torque |
Torque is a turning or twisting action on a body about a rotation axis due to a force F. |
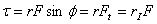 |
|
The total torque on a solid body is the summation of torques exerted by external forces. |
 |
| |
T=Ia is just like F = ma |

Newton’s Second Law in Angular Form: 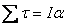
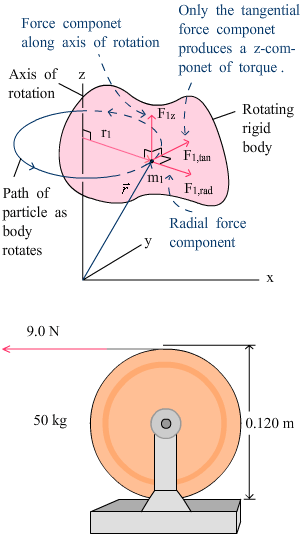
Example: The cable unwinds without stretching or slipping. What is its acceleration?
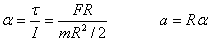
|
 |
|
| |
An unwinding cable |
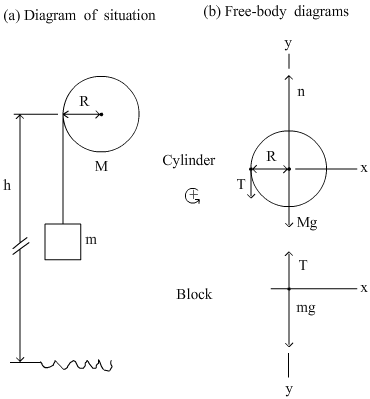
Example: Find the acceleration of the block of mass m.
|
 |
|
|
